
Knee pain occurs in patients of all ages and lifestyles. Such pain is observed during physical activity for various reasons: from injury or decay to significant disease and inflammation. Ignoring this can have serious consequences. A common question is what to do if you are in pain? In order to prevent hospitalization at the first painful sensation, it is recommended to consult a doctor, the treatment should be carried out only by a doctor.
The first manifestation of pain in the knee is usually due to heavy loads, joint wear and deformation. The disease is felt not only during extreme stress, but also at rest, during rest and when performing daily tasks. In this article, we will consider why the knee hurts, the main methods of diagnosis and treatment.
What is the knee joint?
The knee joint of our body carries a large load and body weight; falls account for the majority of injuries and stress during sports and weightlifting. The knee joint itself is one of the largest in our body.
The knee joint includes:
- the merger itself;
- muscles;
- knee cap;
- meniscus;
- joint capsule;
- femur and tibia ends,
- ships,
- nerves
- gardens
Each of these components is susceptible to injury, although pain is not always felt immediately. For example, with a dislocated or torn meniscus and a torn anterior cruciate ligament, mobility will be reduced and vascular damage will cause a hematoma. Infection can begin in the joint capsule of the knee after infectious diseases. If the patient has a neurological disease, a shooting pain may be felt in the knee. In addition, joint pain can radiate to the femur, tibia, and muscles.
Causes of joint pain
According to the nature of pain, it can be divided into two groups: acute and chronic. Acute pain is characterized by rapidly developing and progressive pathologies. Chronic diseases, on the other hand, are quite slow and require lifelong treatment. The causes of such pains are different and the treatment accordingly.
Let's consider the main causes of pain.
Pain due to injuries
The cause of acute pain is injuries and various traumatic actions. You can get injured due to a bad fall, playing sports, or uncomfortable shoes. The pain starts to be felt a few days after the injury. Usually there is a slight swelling in the knee and the victims experience quite excruciating pain. Depending on the severity of the injury, there may be abrasions on the surface of the skin. In addition, excess weight, abuse of bad habits, profession and job characteristics increase the risk of injury.
Types of injuries:
- Knee bruises.Frequent and light damage. Swelling and redness appear in the knee area, the temperature of the surface rises. Even a small injury to the knee can cause the destruction of joint tissue cells.
- Sprains.Sometimes a sprain of a muscle, ligament, or tendon goes unnoticed and causes burning and sharp pain in the knee, and the joint itself becomes unstable when stepping on the foot.
- Ligament tear.It can appear due to strong bending of the foot in an unnatural direction and causes severe pain, swelling and swelling.
- Meniscus tear.It appears due to a heavy load, a blow to the knee, a twisting of the leg and an unnatural position. A torn meniscus causes your feet to not move normally. It often occurs in athletes and is accompanied by swelling, bleeding, and leg stiffness. There is a rule about sports: the knee may hurt, but it should go away in the morning after training. If the disease does not go away, you should consult a doctor.
- Joint fracture.Due to the fracture, soft tissues are also damaged, causing severe pain and deformation of the knee.
Unpleasant sensations in the knee are not always characterized by a disease in this department. Sometimes a herniated disc can cause pain in the knee at night. Discomfort can also occur when the knee joint is underused and the associated muscles lose tone.
Asymmetry of the sacrum and pelvic bones can also provoke the appearance of pain in the knee joint. This occurs as a result of a difference in the length of the lower limbs, which can be the result of congenital characteristics or due to curvature of the pelvis, including scoliosis.
Knee diseases
Any inflammation or damage to the knee structure causes discomfort, especially when moving. And the infection is not always localized in the knee itself. With general joint diseases, the whole body is affected, knees are more damaged due to severe stress. Also, pain in the knee joint can occur with injuries or diseases of the spine or a fracture of the femoral neck. Let's take a look at some of them:
- Arthritisis an inflammatory process that develops after trauma due to infection or metabolic problems. If left untreated, the cartilage of the knee joints gradually wears down, which leads to increased pain.
- Rheumatoid arthritis- an autoimmune disease in which the body's defense cells have a negative effect on the tissue. The joint loses mobility, swelling appears, pain is constantly present and manifests itself with an increased feeling of stiffness.
- Rheumatism- as a rule, teenagers, as well as people who have recently had streptococcal disease, are susceptible to it. It is characterized by changing unpleasant sensations.
- Gonarthrosis (arthrosis).It develops in one or both knees. This disease is characterized by the occurrence of degenerative-dystrophic processes with the growth of connective and bone tissue, which hinders movement. At the beginning of the disease, discomfort begins to be felt only after a long walk, but as the disease progresses, pains begin to appear even after walking short distances. Difficulty getting out of a chair, squatting, or climbing stairs. Pain doesn't just bother you at rest. Destruction or thinning of cartilage shock-absorbing tissue occurs. As gonarthrosis develops, a crisis in the knee and deformation of the joint are noted.
- Reactive arthritis– begins a few days after intestinal infection. Severe pain combined with swelling and redness of the skin over the right or left knee usually indicates reactive arthritis.
- Bursitis– inflammation of the joint capsule, which causes severe pain and discomfort during movement.
- Periarthritis– inflammation of the tendons, muscles and ligaments surrounding the knee joint. Painful sensations appear with increased load on the bent leg.
- Chondropathy– destroys the cartilage surrounding the knee joint and suppresses friction and shock.
- Neoplasms- when they appear, the vessels are compressed, the joint capsule is deformed, causing pain and limiting mobility.
- Osteoporosis- tissues weaken, become more fragile, the amount of calcium in bones gradually decreases.
- Osteomyelitis- inflammation of the bone tissue accompanied by swelling, fever and acute severe pain appears in the damaged area.
- Osteoarthritis– inflammation in the joint capsule is gradually localized to the heads of the bones. Cartilage wears out and thins, causing the bone heads to not slide easily when moving around. Aching pain occurs.
- Osteoarthritis– a disease that affects all components of the joint.
- Patellofemoral pain syndrome- often occurs in young patients. During physical activity, the kneecap moves forward. This happens due to the wrong position of the foot, excessive and heavy loads with unprepared muscles.
- Osgood-Schlatter disease- knee pain when bending, climbing stairs, squatting.
- Nerve damage and disruption of nerve tissue.Shooting pains, numbness and tingling in the lower extremities, loss of mobility appear. A pinched nerve appears due to inflammation, neoplasms or previous injuries. Or neuritis develops - inflammation of the nerve in one or more areas. Severe pain is felt, mobility and sensitivity decrease, the limb contracts involuntarily.
- Violation of blood supply.
- Various other infectious diseases.The resulting complications contribute to the appearance of weakness and pain.
In addition to the listed diseases, others can also contribute to the appearance of pain: synovitis, ligamentitis, tendinitis, gout, neuropathy, cyst and others.
Thus, pain in the knee is always a sign of a pathological process affecting the cartilage, bone or soft tissue structures of the knee itself, or damage to the nerve that innervates it.
Diagnosis of knee pain
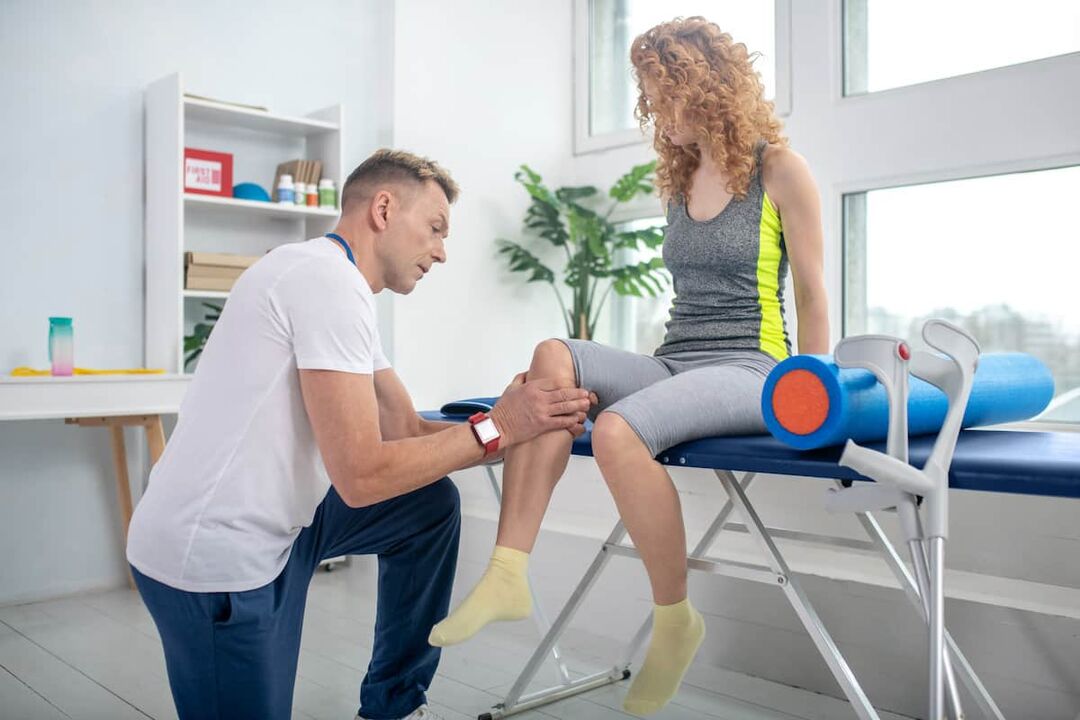

To start the treatment, it is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis from the doctor in the clinic using diagnostic measures.
The patient wants an appointment with an osteopath, orthopedic traumatologist, surgeon or rheumatologist. If necessary, after examination and examination, the patient can be sent to another specialist.
During the admission, the doctor collects an anamnesis - complaints, symptoms and problems, infections and chronic diseases that bother the patient. After that, the doctor can palpate the area of concern and ask the patient to perform various movements and tests. For example, bend and straighten your knee. This will give an initial indication of the extent of the failure.
To obtain additional information and determine the exact diagnosis, the patient is sent to one or more examinations:
- radiography (x-ray);
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- magnetic resonance therapy (MRI);
- computed tomography (CT);
- arthroscopy (a special instrument, an endoscope, is inserted into the joint);
- puncture for collection of synovial fluid;
- laboratory tests (general and biochemical blood tests, serological tests).
Depending on the contraindications, MRI and CT are used to diagnose nerve diseases. Some diagnoses require more specific tests.
You can see an osteopath, physical therapist, chiropractor, or massage therapist for knee pain relief. The osteopath will help restore the normal condition of the pelvic bones and internal organs, which has a positive effect on their activity, improves the nutrition of all spinal structures by activating blood circulation, and improves posture by eliminating spinal deformities.
Treatment of knee pain
It is impossible to choose the best medicine for knee pain yourself. First of all, it is necessary to find the real cause of the symptoms and to determine the type of pathological disorders in the body.
Treatment of the knee joint is carried out comprehensively. This set of measures includes the following:
- medicine (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or chondroprotectors - their effectiveness consists in preserving moisture in cartilage cells, preventing enzymatic action and stopping the degenerative process);
- preparations, solutions for external use;
- osteopathy;
- special exercises and gymnastics, physiotherapy;
- physiotherapeutic methods;
- massages;
- vitamin complexes are drugs indicated to improve metabolic processes in the body.
Various types of physical therapy treatments can be used to treat musculoskeletal conditions that cause knee pain.
Exercise therapy classes are simple and accessible to people of any age, as the individually developed program ensures the creation of a precisely dosed load. Local painkillers are also prescribed for complex therapy, for example, dimethyl sulfoxide ointment (there are contraindications: severe diseases of the kidneys, liver, cardiovascular system, pregnancy, breastfeeding) or anti-inflammatory gel - absorbed immediately. skin, penetrates its deep layers, relieves swelling and pain.
Pain can also be eliminated using high-frequency methods: morphological changes remain, but pain decreases and becomes easier. Also, special orthoses are often prescribed - bandages, knees, splints, tapes, casts and other similar devices. This allows you to transfer the load from the knee and relieve it, reducing the risk of re-injury and promoting rapid rehabilitation. Plasmolifting is rarely used - plasma injections from the patient's own blood directly into the affected knee joint or into the surrounding soft tissue.
Sometimes a bone realignment procedure or surgery is performed (for example, if pieces of bone need to be removed).
The doctor also prescribes pain relievers that do not adversely affect the articular cartilage.
Pay attention to your diet - a balanced diet can prevent inflammation.
If you have a problem with your knee, you should not self-medicate and participate in various procedures to avoid surgical intervention (operation) and possible complications. This attitude can only make the situation worse, and more serious and complex therapy will be required. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor who will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment, procedures and effective drugs. Take care of yourself and your health!























